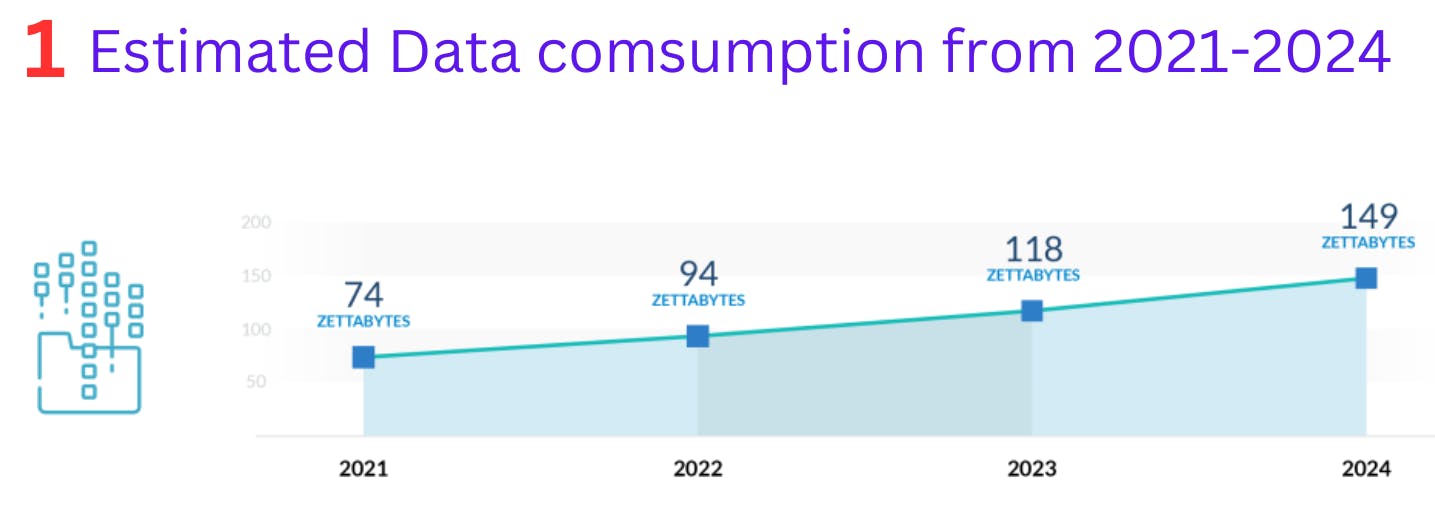
Big Data contains a large amount of data that is not being processed by traditional data storage or the processing unit. It is used by many multinational companies to process the data and business of many organizations. The data flow would exceed 150 exabytes(1,000,000 TB) per day before replication.
Big Data Characteristics
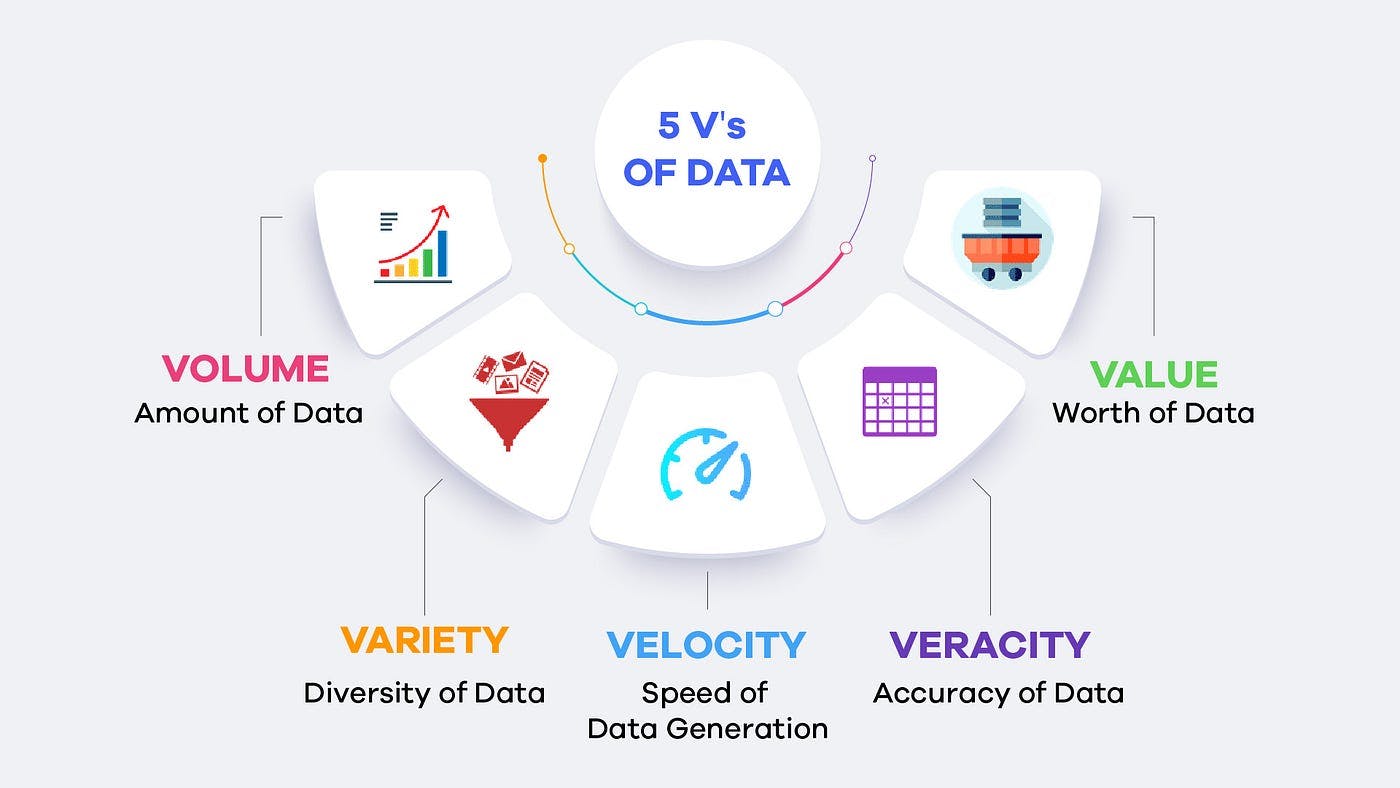
There are 5 main characteristics of Big data
Volume
Variety
Veracity
Velocity
Value
1. Volume
Volume refers to the sheer size of data. Big data involves massive amounts of data.
Ex: Terabytes, petabytes of data generated by different sources such as social media platforms, business processes, human interactions, and many more.
2. Variety
Variety refers to the diversity of data – structured data, unstructured data, and semi-structured data.
Ex: database, JSON data, data generated by social media, etc.
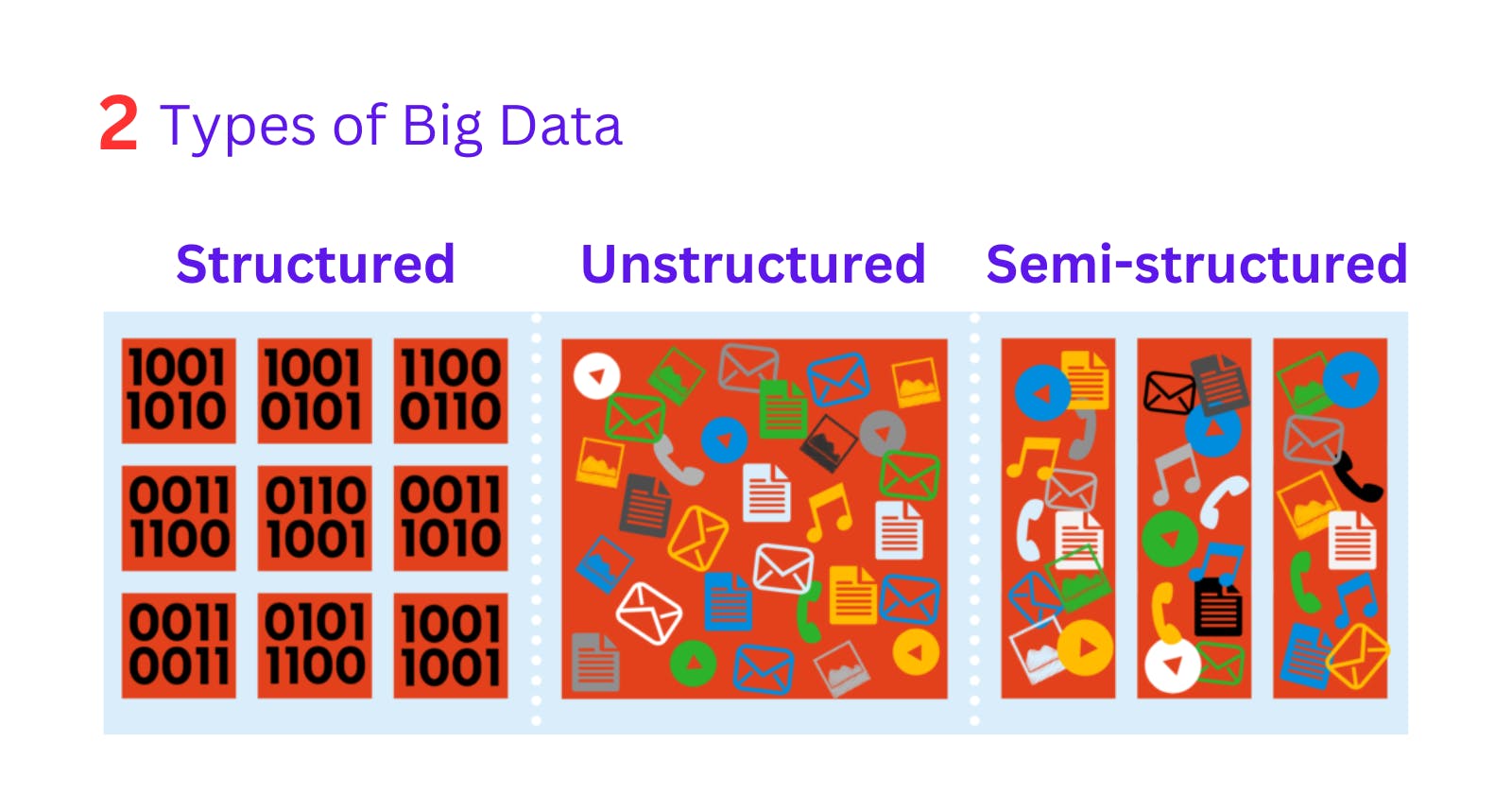
- Structured data is well-organized data bounded in rows and columns. It is a type of data we are most familiar with in our daily life. All structured query languages can be considered structured language. It is also called relational data.
Ex: SQL, spreadsheets, organized database.
- Unstructured data is data that does not have any definite schema or set of rules. Its arrangements are unsettled and unplanned. It includes different data types and formats. It requires efficient software tools to analyze.
Ex: video, images, social media posts, etc.
- Semi-structured data is partially organized and may contain tags, markers, or elements that separate the data. It is also called NoSQL data. It mostly has key-value pairs data.
Ex: JSON, zip file, XML file, etc
3. Veracity
Veracity refers to the quality and reliability of data.
Ex: data uncertainty, an inconsistency which is very common in real-world data.

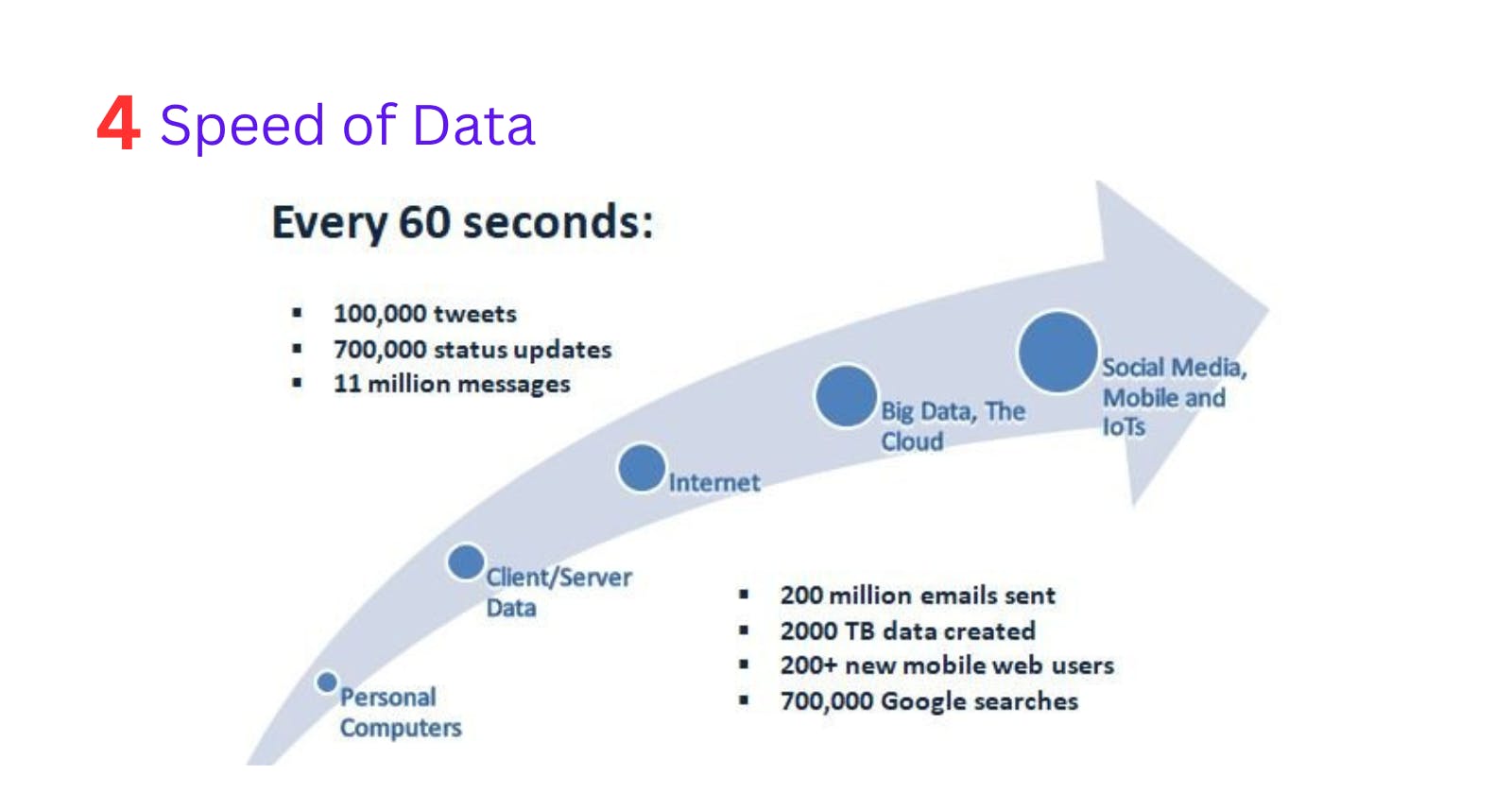
4. Velocity
Velocity signifies the speed of the data at which it is generated and the speed at which it gets delivered.
Ex: real-time live stream on social media such as YouTube live-stream.
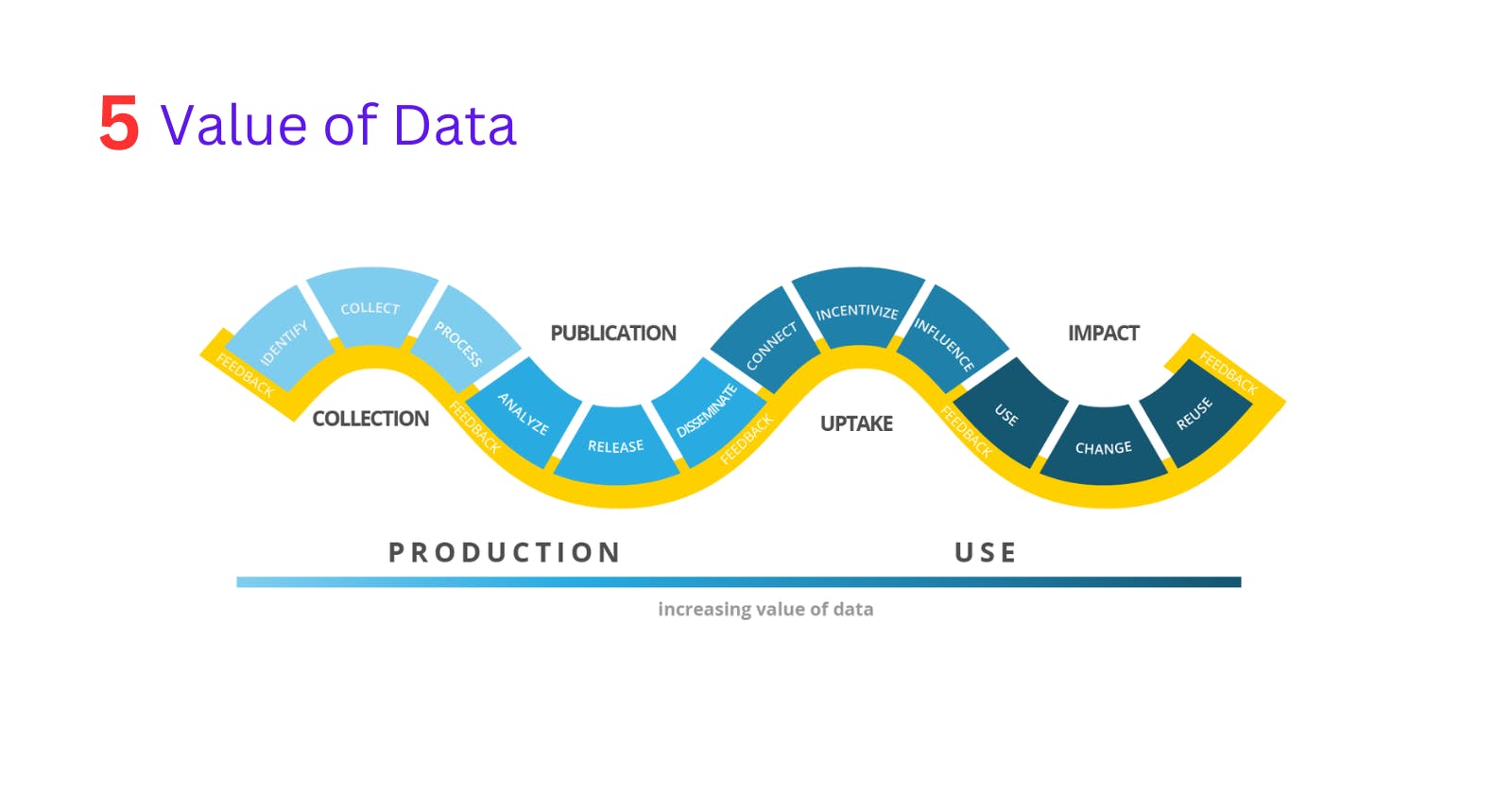
5. Value
Value represents the insights that are delivered from Big data.
Ex: extracting meaning of full patterns and trends and actionable insights that can drive business or research advancements.